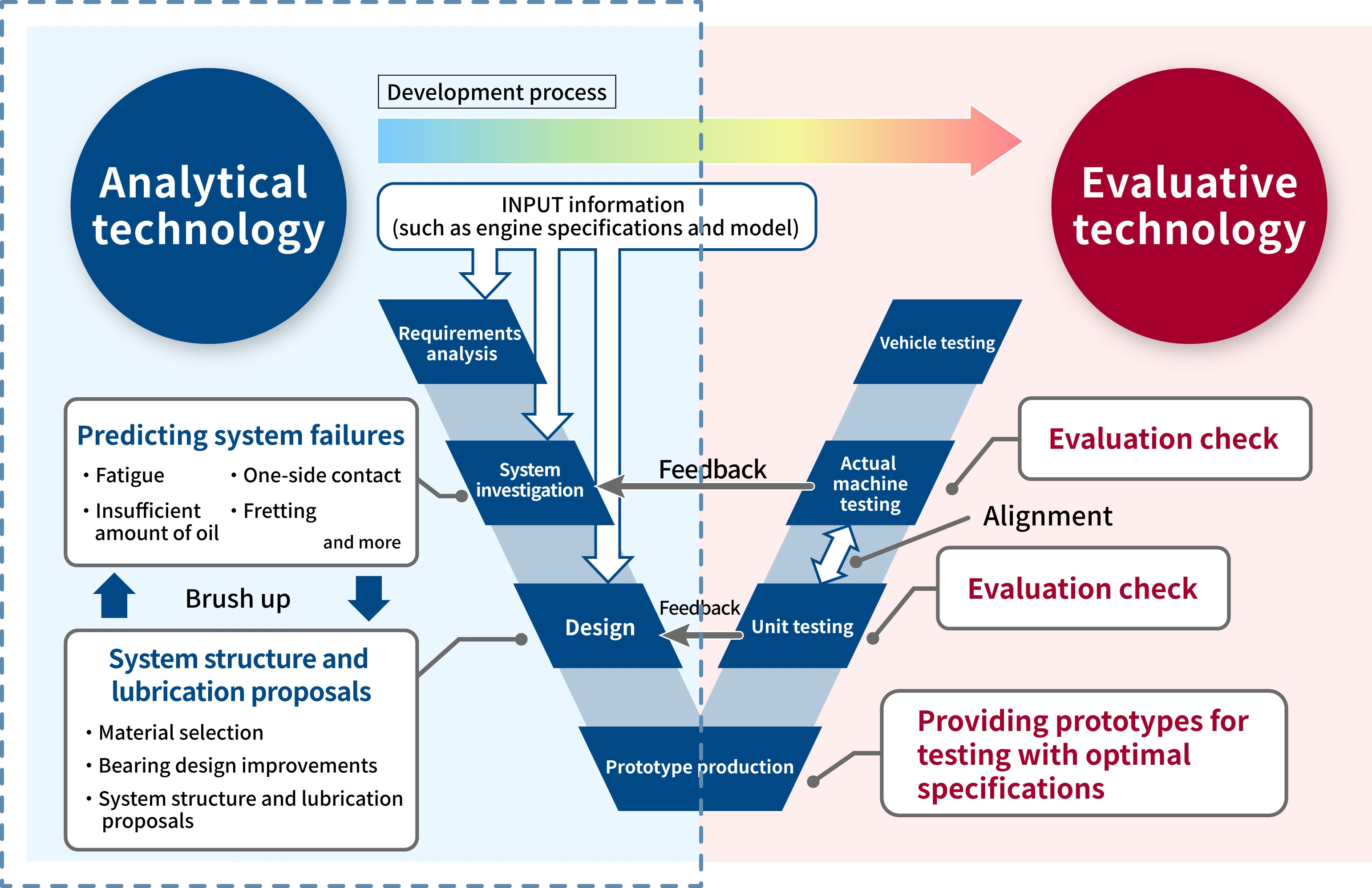
Analytical CAE
We propose optimal specifications by completing design investigations in the upstream section of the V process.
Analyses and simulations, which are upstream processes in the V process, and unit testing and evaluations of actual machines, which are downstream processes, are all performed in-house. Directing feedback of evaluation results into the analytical technology makes it possible to improve the strength and precision of model-based development (MBD). Accordingly, we can propose highly accurate and optimal materials from the initial stages of development and thereby help clients speed up the development process and reduce man-hour requirements.

Examples of analysis
Predicting the state of one-side contact
The state of one-side contact subsequent to an evaluation of durability can be accurately predicted with the performance of lubrication analysis that takes elastic deformation of the entire engine into account.

| Related pages | Seizure criteria analysis |
|---|
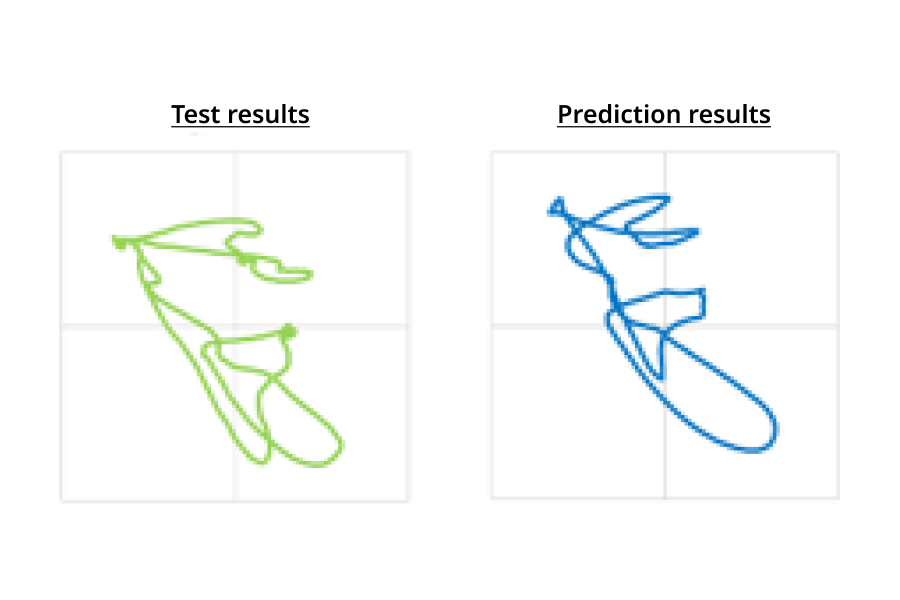
Predicting the trajectory of the axial center
The trajectory of the axial center during actual operations can be accurately predicted and noise and vibrations attributable to the behavior of the crankshaft can be analyzed.
| Related pages | Initiatives for the development of analytical and evaluative technologies |
|---|
Deformation/stress analysis during assembly
Assembly analysis that takes the rigidity of the structure and the bolt axial force into account allows the deformation, stress, and strain at the time of assembly to be accurately analyzed.

| Related pages | Initiatives for the development of analytical and evaluative technologies |
|---|
Predicting friction
The instantaneous friction acting on the crankshaft where actual operations are assumed can be accurately predicted. This helps to lower friction without a loss of lubrication performance exhibited by the sliding parts.

3D gas-liquid two-phase fluid analysis
Multiscale spaces ranging from the micron order to the millimeter order can undergo unsteady fluid analysis in three dimensions and by taking gas-liquid two-phase conditions into account.

| Related pages | 3D lubrication analysis and wear analysis |
|---|
Thermal stress analysis
Stress and strain due to heat input into the structure can be accurately analyzed. This enables the impact of high-temperature gas and molten metal flow to be taken into account and also helps in investigating die-cast designs.

Thermal fluid analysis
The coupling of fluid behavior and heat conduction enables the distribution of heat in a structure to be accurately analyzed. This helps in investigating the optimization of the cooling blower during battery operations.


