Background
An initiative to accommodate higher in-cylinder pressure as a way to comply with regulations governing diesel engine emissions and fuel consumption
→Slide bearings for engines help to accommodate higher contact pressure values

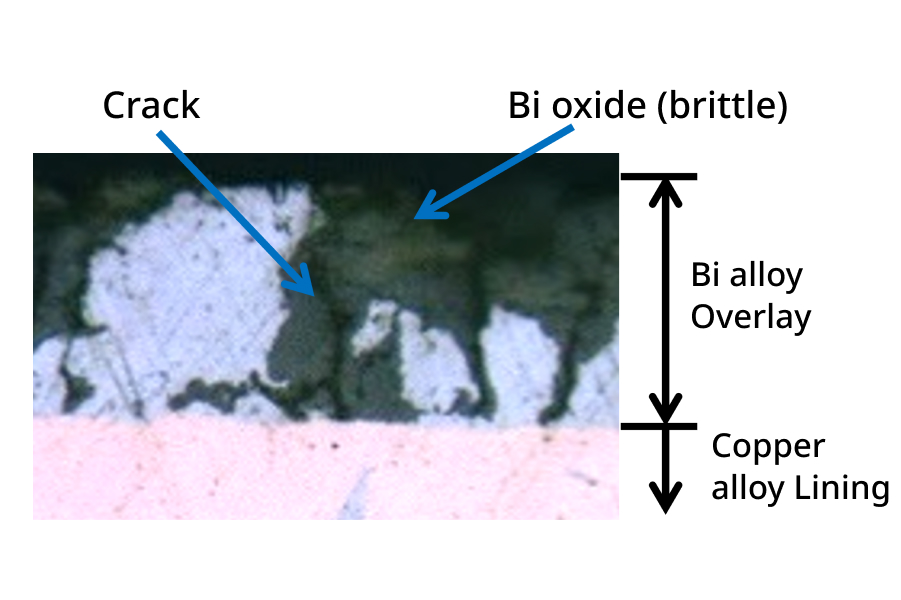
Issues pertaining to Bi-alloy overlay bearings
- Bismuth (Bi) on its own exhibits low mechanical strength, such that fatigue damage occurs.
- Bi oxides are created at high working temperatures or in an environment of prolonged operations.
→By forming a Bi-Sb alloy, dramatic improvements in terms of fatigue resistance and oxidation resistance are achieved.
Bi :bismuth
Sb:antimony
Description of development
The world’s first adoption of a Bi-Sb alloy for overlay bearings.
- Antimony (Sb) is an element that does not lower the melting point, which would affect high-temperature strength, and that enables electroplating.

by a factor of two.
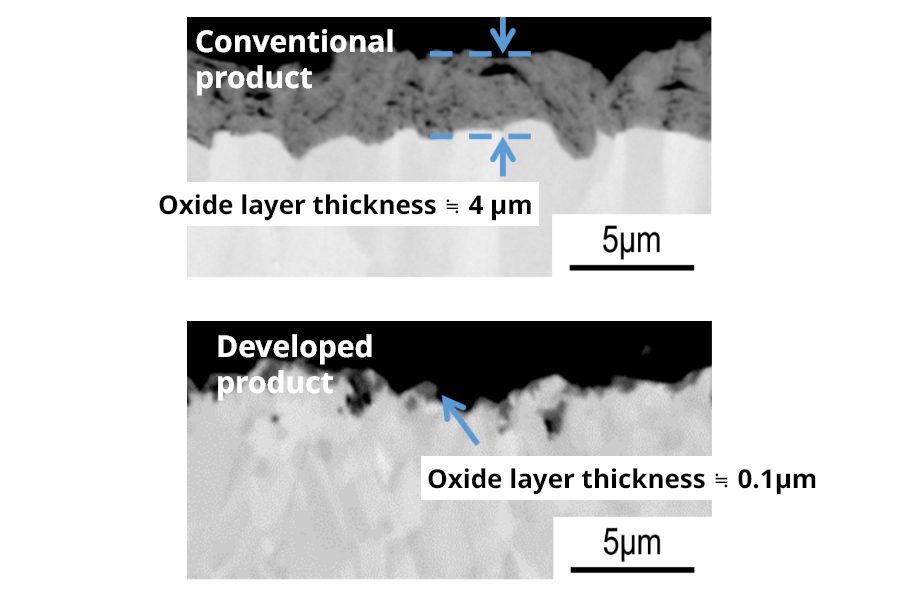
Results of XPS analysis

Fatigue resistance is also improved for copper alloy linings.
- Adding tin (Sn) and nickel (Ni) as solute strengthening elements improves fatigue and corrosion resistance.
- Adding bismuth (Bi), which has a solid lubricating effect, and silver (Ag), which produces Sn compounds with low adhesion properties, ensures seizure resistance.
Effect
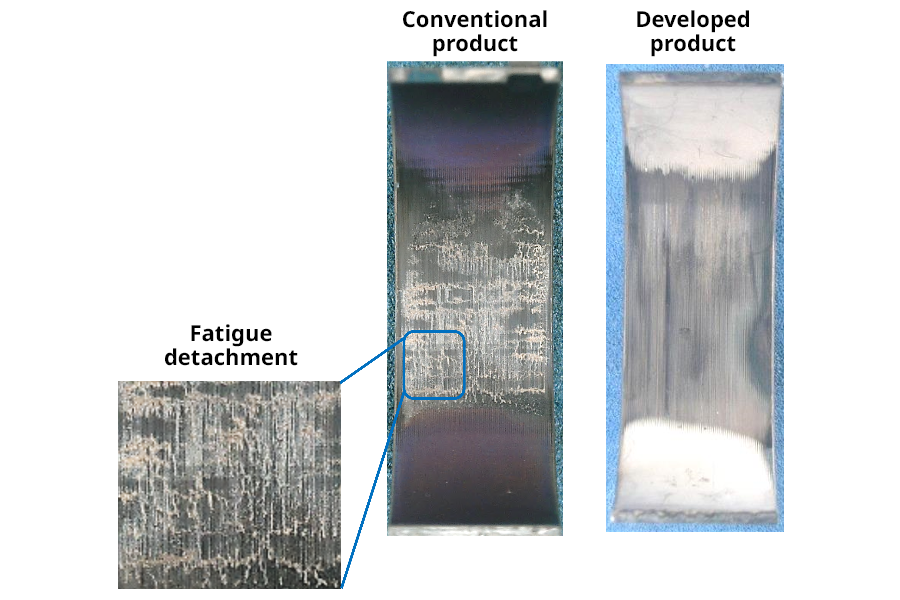
Fatigue resistance
Fatigue test results
Oxidation resistance
Results of heating test conducted in oil
Seizure resistance
Results of seizure test
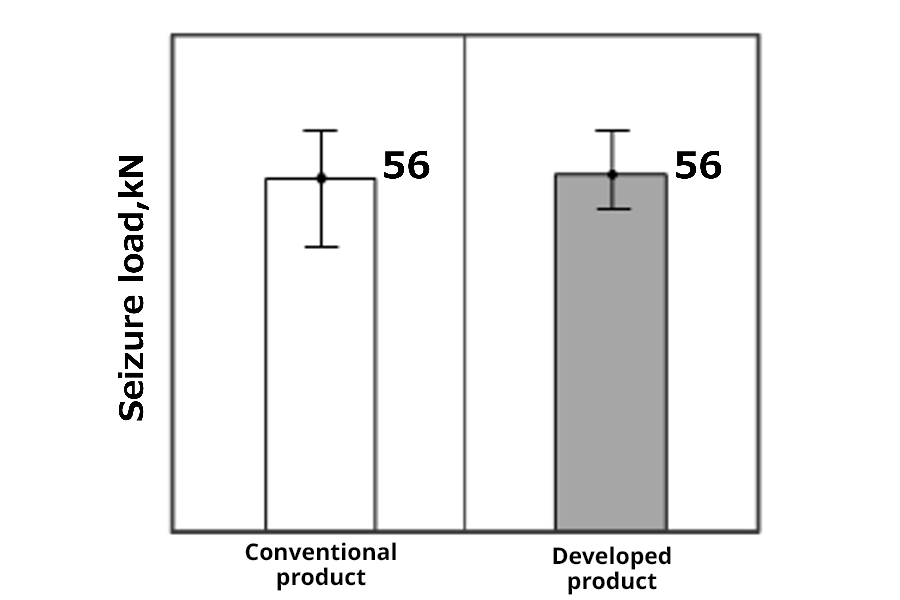
No sign of any reduction in seizure resistance

